We are surrounded by virus and bacteria. In fact some 800 million fall at your feet, consistently, when you walk down the street.
So everyone for the past three years has been losing their minds over one crummy virus—one of the coronavirus which by the way, has been around person kind for over 25,000 years!
Obviously, then, the BIG question is: Why aren’t we all sick and dying? All the time??
Your immune system. Its ingenious design filters out most of ‘non-self’ cells like virus, bacteria and fungi to some extent and does it all without you knowing a thing, for the most part.
If an infectious organism manages to enter the body, the immune system kicks into gear to try to eliminate it. White blood cells, also known as leukocytes, are an important part of the immune system and play a key role in fighting infections. There are several different types of white blood cells, each with a specific role in the immune response.
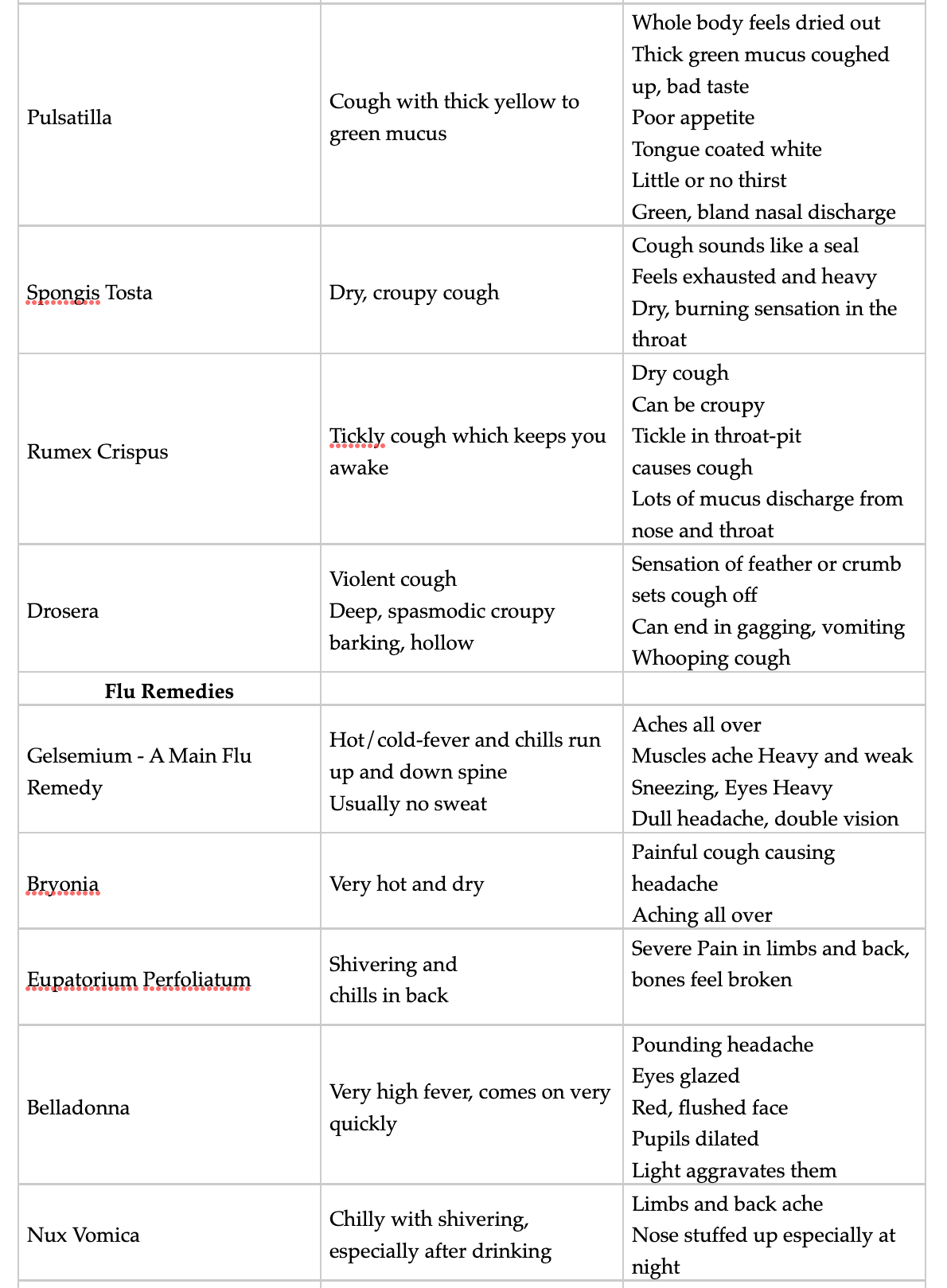
Note: Scroll down for a chart on how to use homeopathics to treat Cold & Flu and also lists of supplements (US and Canada) for Cold & Flu Prevention and Treatment
T-Cells
One type of white blood cell, called a T-lymphocyte, or T-cell, plays a crucial role in the immune response to viruses. T-cells can recognize and kill infected cells, and they can also release chemicals called cytokines that help to coordinate the immune response.
There are several different types of T-cells, or T-lymphocytes, each with a specific role in the immune response.
Helper T-cells: Helper T-cells, also known as CD4+ T-cells, help to coordinate the immune response. They do this by releasing chemicals called cytokines that help to activate other immune cells, such as B-cells and killer T-cells.
Killer T-cells: Killer T-cells, also known as CD8+ T-cells, are responsible for directly killing infected cells. They do this by recognizing and binding to specific proteins called antigens, which are displayed on the surface of infected cells. Once they have bound to the infected cell, they can release toxic substances that kill the cell.
Regulatory T-cells: Regulatory T-cells, also known as Tregs, play a role in regulating the immune response. They can help to suppress the activity of other immune cells and prevent an excessive immune response. This is important to prevent the immune system from attacking the body's own tissues, which can lead to autoimmune diseases.
Memory T-cells: Memory T-cells are T-cells that remain in the body after an infection has been resolved. They "remember" the specific pathogens that they encountered, and if the body is exposed to the same pathogen in the future, the memory T-cells can quickly respond and help to clear the infection.
B-Cells
Another type of white blood cell, called a B-lymphocyte, or B-cell, is responsible for producing proteins called antibodies. Antibodies are specific to a particular pathogen and can recognize and bind to it, marking it for destruction by other parts of the immune system.
The process is: when a pathogen, such as a virus or bacteria, enters the body, B-cells can recognize and bind to specific proteins called antigens that are displayed on the surface of the pathogen. This process is called antigen recognition.
Once a B-cell has recognized and bound to an antigen, it becomes activated and begins to divide, producing a large number of identical copies of itself, called clones. Some of these clones mature into plasma cells, which produce large quantities of a specific protein called an antibody.
Antibodies are proteins that are specific to a particular pathogen and are capable of recognizing and binding to it. They can mark the pathogen for destruction by other parts of the immune system, such as by attracting the attention of killer T-cells or by activating the complement system, which is a group of proteins that can punch holes in the pathogen's cell membrane, causing it to die.
In addition to producing antibodies, B-cells can also present antigens to T-cells, which can help to activate the T-cells and coordinate the immune response.
Non-Neutralizing Antibodies
This is something I have to mention here as it plays a HUGE role in how bad the mRNA jabs are. They result in the production of non-neutralizing antibodies..and are certainly not good for your health. Non-neutralizing antibodies are antibodies that are produced in response to an infection or the mRNA jab, but which do not have the ability to neutralize the pathogen. This means that they are unable to prevent the pathogen from replicating or from causing illness.
While non-neutralizing antibodies can be produced in response to many different types of infections, they are of particular concern in the context of viral infections. This is because many viruses, such as HIV and influenza, can mutate rapidly and evolve to evade the immune response. If the immune system produces non-neutralizing antibodies in response to a viral infection, the virus can continue to replicate and spread, potentially leading to more severe illness.
There are several possible reasons why non-neutralizing antibodies may be produced in response to a viral infection. One reason is that the virus may mutate and change the structure of its surface proteins, which can make it more difficult for the immune system to recognize and neutralize it. Another reason is that the immune system may produce a low level of neutralizing antibodies, which is not enough to fully control the infection.
Overall, non-neutralizing antibodies can be harmful because they are unable to prevent a pathogen from replicating or causing illness, and may even contribute to the severity of the infection.
Non-neutralizing antibodies are antibodies that do not neutralize the virus, meaning they do not prevent the virus from infecting cells. Non-neutralizing antibodies can still play a role in the immune response to viral infection, however. For example, they may help to activate immune cells such as macrophages, which can then help to clear the virus from the body. However, non-neutralizing antibodies can also contribute to more severe viral infection in some cases. This can occur when the antibodies actually enhance the ability of the virus to infect cells, a phenomenon known as "antibody-dependent enhancement." This can happen when the virus uses the antibodies to "coat" itself, allowing it to more easily enter cells and thereby increasing the severity of the infection. This phenomenon has been observed with some viruses, including coronaviruses, dengue viruses, and HIV.
Below are the list of supplemental support I suggest to my patients. Use what makes sense to you and don’t hesitate to contact me here with questions.
Cold & Flu Support for US Citizens:
Cold & Flu Support for Canadian Citizens:
Homeopathic Remedies:
Here are charts of the remedies I use most often in my practice. The usual dosing is to use a 30C strength, three times per day. If you’re using more than one, and that’s common, separate them by 10 minutes or so.
Remember, all homeopathics must be taken in a clean mouth, no food or drink residues or toothpaste. You should have no flavours in your mouth on dosing.